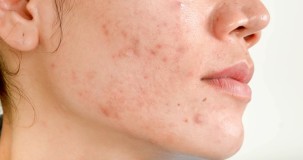
 Symptoms
Symptoms
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Baby
Baby
 Baby
Baby
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Benefits
Benefits
 Benefits
Benefits
Can drinking too much water lower potassium? Can excessive water intake lead to potassium depletion? Find out if drinking too much water can lower potassium levels in this informative blog post.
As a specialized content creation and marketing expert, it is essential to provide accurate and informative articles to address various topics. One such topic that often raises concerns is whether drinking excessive amounts of water can lower potassium levels. In the following article, we will explore this potential relationship and shed light on the facts.
Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining various bodily functions. It helps regulate fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. Adequate potassium levels are crucial for overall health and well-being.
Water, on the other hand, is the essence of life, and staying hydrated is essential for proper bodily functions. It is often recommended to drink an adequate amount of water each day to maintain good health. However, when it comes to potassium levels, it is crucial to strike the right balance.
There is a condition called water intoxication, also known as hyponatremia, which occurs when an individual consumes an excessive amount of water. This condition can indeed cause a decrease in potassium levels, among other electrolytes in the body.
Water intoxication typically occurs when someone drinks a significantly excessive amount of water within a short period. This can happen during events like endurance sports or extreme water drinking competitions. However, it is relatively rare and unlikely to occur in everyday situations where individuals consume water as per their thirst and hydration needs.
The reason water intoxication can lead to lowered potassium levels is that excessive water consumption puts pressure on the kidneys to eliminate the excess through urine. As the kidneys work to excrete the excess water, they may also remove essential electrolytes, including potassium.
It is worth noting that for most people, maintaining a balance between water intake and potassium levels is not a cause for concern. The human body is designed to regulate its fluid and electrolyte levels efficiently, ensuring overall well-being. However, certain individuals may be more susceptible to imbalances.
People with specific medical conditions, such as kidney disease or adrenal gland disorders, may have impaired potassium regulation in their bodies. For these individuals, excessive water intake could potentially further disrupt their electrolyte balance and cause a decrease in potassium levels.
In general, a balanced and healthy diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and other potassium-rich foods is enough to maintain adequate potassium levels for the average person. Drinking plenty of water, within reasonable limits, is essential for overall hydration and well-being.
In conclusion, while excessive consumption of water can, in rare cases, lead to a decrease in potassium levels, it is not a common concern for most individuals. Maintaining a balanced diet and drinking an appropriate amount of water for your daily needs will help ensure your potassium levels remain within a healthy range.
Remember, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice if you have any concerns or specific health conditions. Stay hydrated, stay informed, and prioritize your overall well-being.
No, excessive water consumption does not directly cause low potassium levels in the body. However, excessive water intake without balanced electrolyte consumption can dilute the levels of potassium, resulting in a relative deficiency. It is important to maintain a balanced diet and not rely solely on water intake for electrolyte replenishment.
2. Does drinking more water cause potassium depletion?No, drinking more water does not directly cause potassium depletion. Potassium depletion is usually a result of factors such as excessive sweating, prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. It is essential to maintain a healthy diet and consult a healthcare professional if experiencing potassium depletion symptoms.
3. How does excessive water intake affect potassium levels?Excessive water intake alone does not affect potassium levels. However, if someone consumes excessive amounts of water without consuming enough potassium-rich foods, it may result in dilution of potassium levels in the blood. This is why it is important to maintain a balanced diet and ensure adequate potassium intake alongside proper hydration.
4. Can drinking too much water cause potassium deficiency?Drinking too much water alone does not cause potassium deficiency. However, excessive water intake without simultaneous consumption of potassium-rich foods can lead to dilution of potassium levels. To prevent potassium deficiency, it is crucial to maintain a balanced diet and ensure adequate intake of potassium along with proper hydration.
5. Is there a connection between excessive water consumption and low potassium?While excessive water consumption itself does not cause low potassium levels, it can indirectly contribute to potassium dilution. If someone excessively consumes water without consuming enough potassium-rich foods, it may result in lower concentrations of potassium in the blood. To maintain a healthy balance, it is recommended to consume a well-rounded diet that includes sufficient potassium and maintain proper hydration.
 LATEST ARTICLES
LATEST ARTICLES

At what stage in pregnancy does heartburn start?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong?

Can constipation hurt the baby during pregnancy?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong if taken too early?

Can a pregnancy test read wrong?

Are meds safe during pregnancy?

Can a UTI cause a false positive pregnancy test?

Can breasts be sore without pregnancy?

Can 2 faint positive pregnancy tests be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test change to positive after 10 mins?

Can a pregnancy test be positive one day and negative the next?

Can corpus luteum cyst cause positive pregnancy test?

Can a pregnancy be successful with low hCG?

Are pregnancy tests accurate at night?

Can a pregnancy test lie about being positive?

Are pregnancy bumps hard or soft?

Can clearblue detect 1 week pregnancy?

Are you dry in early pregnancy?

Can bananas cause heartburn during pregnancy?

Can autism be detected during pregnancy?

Can a positive pregnancy test can be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test be positive at 1 week?

Can AFE happen during pregnancy?
 POPULAR ARTICLES
POPULAR ARTICLES

Am I bloated or just fat?
Am I bloated or do I have an ovarian cyst?

Am I bloated or fat?

Are blackouts a symptom of depression?
Are blisters symptoms of diabetes?
Are blackouts a symptom of anxiety?

Are apples good for pregnancy?

Are any medications Pregnancy Category A?

Are bananas good for pregnancy?

Are baby kicks stronger at 20 weeks?