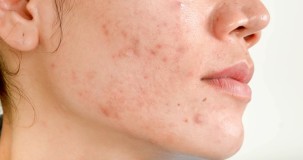
 Symptoms
Symptoms
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Baby
Baby
 Baby
Baby
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Benefits
Benefits
 Benefits
Benefits
Can balanitis stay for years? Balanitis can persist for years without proper treatment, causing chronic inflammation and discomfort. Learn more about this condition and its long-term impact.
Why does balanitis persist?
There are several reasons why balanitis may persist for an extended period:
1. Recurrent infections: If the underlying cause of balanitis is a bacterial or fungal infection, it can recur if not properly treated. The persistent presence of the infecting organism can lead to chronic inflammation of the glans, resulting in long-lasting symptoms.
2. Poor hygiene: Inadequate cleansing of the penis can lead to the accumulation of dirt, dead skin cells, and smegma, which can create a favorable environment for bacterial growth. If proper hygiene practices are not followed, the inflammation caused by balanitis may continue for an extended period.
3. Skin conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as psoriasis or eczema, can affect the genital area, including the glans. These conditions can cause persistent inflammation and discomfort, leading to long-term balanitis if left untreated.
4. Diabetes: Diabetes weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. If a person with diabetes develops balanitis, it may take longer to resolve due to compromised immune function.
5. Allergic reactions: Some individuals may have an allergic reaction to certain substances, such as soaps, lotions, or latex condoms, which can cause persistent inflammation. Identifying and avoiding the allergen is essential to resolving the balanitis symptoms.
How can balanitis be treated?
The treatment of balanitis depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, practicing good hygiene and keeping the area clean and dry is sufficient to resolve the inflammation. This includes gentle cleansing with warm water and mild, fragrance-free soap.
Antifungal or antibacterial medications may be prescribed if an infection is identified. These medications can help eliminate the infecting organism and reduce inflammation. In some cases, topical corticosteroids may be recommended to reduce inflammation and itching.
If balanitis persists for an extended period, a consultation with a healthcare professional is necessary. The healthcare provider can evaluate the symptoms, perform appropriate tests if needed, and suggest further treatment options. In some cases, a referral to a dermatologist or urologist may be required for specialized care and management.
Preventing balanitis recurrence:
Prevention plays a vital role in avoiding the persistence of balanitis:
1. Maintain proper personal hygiene: Regularly clean the genital area, especially the glans, to minimize the risk of infection and inflammation. Avoid using harsh soaps or cleansers that can disrupt the natural balance of the skin.
2. Avoid irritants: Identify and avoid substances that may trigger an allergic reaction or irritation. This can include certain soaps, chemicals, lotions, or even specific fabrics.
3. Treat underlying medical conditions: If balanitis is a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or a skin condition, it is important to manage and treat that condition effectively to prevent balanitis from persisting.
Conclusion:
Balanitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the glans. While most cases are temporary and easily treated, some individuals may experience long-term balanitis. It is crucial to identify and address the underlying cause to prevent the persistence of symptoms. Maintaining good personal hygiene, seeking appropriate medical care, and following prevention measures are essential in managing and preventing balanitis.
Yes, balanitis can potentially become a chronic condition that lasts for years if left untreated or if the underlying causes are not managed properly.
2. What are the common signs and symptoms of balanitis?Some common signs and symptoms of balanitis include redness, swelling, itching, pain, rash, discharge, and an unpleasant odor in the genital area.
3. What are the possible causes of balanitis?Balanitis can be caused by various factors such as poor hygiene, skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, irritation from chemicals or irritants, infections (bacterial, fungal, or viral), diabetes, and certain medications or allergies.
4. How is balanitis typically treated?The treatment for balanitis depends on the underlying cause. It may include improved hygiene practices, topical creams or ointments, oral medications, antifungal treatments, steroid creams, antibiotics, and management of any existing medical conditions like diabetes.
5. Can balanitis be prevented?Yes, there are steps you can take to help prevent balanitis. These include maintaining proper genital hygiene, avoiding irritants and harsh chemicals in the genital area, wearing loose-fitting underwear, managing underlying medical conditions, practicing safe sex, and avoiding prolonged exposure to moisture or dampness in the genital area.
 LATEST ARTICLES
LATEST ARTICLES

At what stage in pregnancy does heartburn start?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong?

Can constipation hurt the baby during pregnancy?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong if taken too early?

Can a pregnancy test read wrong?

Are meds safe during pregnancy?

Can a UTI cause a false positive pregnancy test?

Can breasts be sore without pregnancy?

Can 2 faint positive pregnancy tests be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test change to positive after 10 mins?

Can a pregnancy test be positive one day and negative the next?

Can corpus luteum cyst cause positive pregnancy test?

Can a pregnancy be successful with low hCG?

Are pregnancy tests accurate at night?

Can a pregnancy test lie about being positive?

Are pregnancy bumps hard or soft?

Can clearblue detect 1 week pregnancy?

Are you dry in early pregnancy?

Can bananas cause heartburn during pregnancy?

Can autism be detected during pregnancy?

Can a positive pregnancy test can be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test be positive at 1 week?

Can AFE happen during pregnancy?
 POPULAR ARTICLES
POPULAR ARTICLES

Am I bloated or just fat?
Am I bloated or do I have an ovarian cyst?

Am I bloated or fat?

Are blackouts a symptom of depression?
Are blisters symptoms of diabetes?
Are blackouts a symptom of anxiety?

Are apples good for pregnancy?

Are any medications Pregnancy Category A?

Are bananas good for pregnancy?

Are baby kicks stronger at 20 weeks?