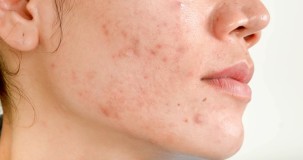
 Symptoms
Symptoms
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Baby
Baby
 Baby
Baby
 Pregnancy
Pregnancy
 Benefits
Benefits
 Benefits
Benefits
Are mammary glands the same as nipples? No, mammary glands are not the same as nipples. Mammary glands are the organs that produce milk in mammals, while nipples are the raised areas on the surface of the mammary glands where milk is released.
Mammary glands are specialized organs found in mammals that produce milk to nourish offspring. These glands are prominent in female mammals but can also be present in males to a lesser extent. In humans, mammary glands are located in the breasts. They undergo significant changes during puberty, pregnancy, and lactation.
Nipples, on the other hand, are the small, protruding structures located on the surface of the breasts. They are primarily responsible for delivering milk to the offspring during breastfeeding. Nipples contain numerous nerve endings that provide sensory feedback and facilitate the suckling reflex in newborns. They come in various shapes, sizes, and colors.
While mammary glands are present in both males and females, the functional significance of nipples differs between the sexes. In females, nipples serve as the exit points for milk produced by the mammary glands. In males, nipples do not typically produce milk and their functional role remains mostly vestigial.
During breastfeeding, hormones trigger the release of milk from the mammary glands into the ducts, which then exit through the nipples. The baby latches onto the nipple to initiate suckling and stimulates milk production through sucking motions. This process is essential for providing proper nutrition to newborns and is often accompanied by a strong bond between mother and child.
Mammary glands and nipples have evolved over millions of years as a result of natural selection. The ability to produce milk and breastfeed offspring has proven to be a successful reproductive strategy for mammals. While some mammals possess multiple pairs of mammary glands, humans typically have two. The presence of nipples on the breasts provides a convenient and efficient way to deliver milk to the young.
In summary, mammary glands and nipples are closely related anatomical structures but serve distinct functions. Mammary glands produce milk, while nipples act as the outlets for that milk. Understanding the physiology and biology of mammary glands and nipples is crucial for biology and health-related fields. The ability to breastfeed is a defining characteristic of mammals and plays a vital role in the survival and development of their young.
No, mammary glands and nipples are not the same thing. Mammary glands are the actual glands responsible for producing milk in mammals, while nipples are the external protrusions through which milk is secreted.
2. Do all mammals have mammary glands and nipples?Yes, all female mammals have mammary glands and nipples. However, the size and location of these glands may vary depending on the species.
3. Can males have mammary glands and nipples too?While males do possess nipples, their mammary glands are usually undeveloped and do not function in milk production. However, in rare cases, some male mammals, including humans, may develop functional mammary tissue due to certain hormonal imbalances.
4. Are nipples necessary for breastfeeding?Yes, nipples are crucial for breastfeeding in mammals. They provide a passage for the milk to pass from the mammary glands to the offspring. The shape and size of nipples may vary across different species to facilitate efficient breastfeeding.
5. Are all nipples the same in terms of appearance and function?No, nipples vary widely in appearance and function across different species. Some mammals have multiple nipples, while others may have a single pair. Additionally, the structure, size, and color of nipples also differ, depending on the species.
 LATEST ARTICLES
LATEST ARTICLES

At what stage in pregnancy does heartburn start?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong?

Can constipation hurt the baby during pregnancy?

Can a pregnancy test be wrong if taken too early?

Can a pregnancy test read wrong?

Are meds safe during pregnancy?

Can a UTI cause a false positive pregnancy test?

Can breasts be sore without pregnancy?

Can 2 faint positive pregnancy tests be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test change to positive after 10 mins?

Can a pregnancy test be positive one day and negative the next?

Can corpus luteum cyst cause positive pregnancy test?

Can a pregnancy be successful with low hCG?

Are pregnancy tests accurate at night?

Can a pregnancy test lie about being positive?

Are pregnancy bumps hard or soft?

Can clearblue detect 1 week pregnancy?

Are you dry in early pregnancy?

Can bananas cause heartburn during pregnancy?

Can autism be detected during pregnancy?

Can a positive pregnancy test can be wrong?

Can a pregnancy test be positive at 1 week?

Can AFE happen during pregnancy?
 POPULAR ARTICLES
POPULAR ARTICLES

Am I bloated or just fat?
Am I bloated or do I have an ovarian cyst?

Am I bloated or fat?

Are blackouts a symptom of depression?
Are blisters symptoms of diabetes?
Are blackouts a symptom of anxiety?

Are apples good for pregnancy?

Are any medications Pregnancy Category A?

Are bananas good for pregnancy?

Are baby kicks stronger at 20 weeks?